A Translocation May Lead to Cancer if It
The simplest examples of cancers with dysregulated development are perhaps hematopoietic malignancies in which a differentiation program is stalled before the cells reach their. Mutations in the genes RET VHL NF1 SDHA SDHB SDHC SDHD SDHAF2 MDH2 IDH1 PHD1 PHD2 HIF2A EPAS1 2 TMEM127 MAX HRAS MAML3 and CSDE1 may play a role in forming pheochromocytoma and paragangliomas.

Chap 24 Cancer Topics Goals Tumor Cells And The Onset Of Cancer Ppt Video Online Download
If you have had two or more losses you and your partner should consider a karyoptype to check for a balanced translocation.
. An important aspect of Akts promotion of cell survival involves alterations in cellular energy metabolism 168 169. Scientists have found mutations in approximately 20 different genes that they think may lead to pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. In its sporadic form individuals normally have two functional copies of the RB1 gene in each of their cells and require two.
But there is a risk of unbalanced gametes that lead to miscarriages or abnormal offspring. The fact that continuous irritation over long periods of time can lead to cancer had already been described in the. The logic being that the.
These may be induced into a stem-cell-like state by an oncogenes or a normal stemprogenitor cell may be the cell-of-origin that sustains the successive mutations that lead to malignancy. This is known as a translocation Downs. A gene fusion may be created when the translocation joins two otherwise-separated genes.
Translocation is one type of gene rearrangement. In addition Akt promotes nuclear translocation of the ubiquitin ligase MDM2 which counteracts p53-mediated apoptosis. To be an independent genetic event from both the episomal NUP214-ABL1 amplification and the NOTCH1 mutations but may lead to the activation of other putative regulatory genes in the 9q34 region.
This translocation t1122 fuses part of the EWSR1 gene from chromosome 22 with part of the FLI1 gene from chromosome 11 creating the EWSR1FLI1 fusion gene. These tumors develop in bones or soft tissues such as nerves and cartilage. In cases of familial retinoblastoma it is common for affected individuals to develop multiple tumors because of the relatively high probability of this second mutation occurring.
In some cases of recurrent pregnancy loss in vitro fertilization with preimplantation genetic testing may be considered. A translocation involving chromosome 11 can cause a type of cancerous tumor known as Ewing sarcoma. This translocation and its variant t1214.
The chance of finding a balanced translocation in either parent is 4. Some of the patients with the 9q34dup also had NUP214-ABL1 episomal amplification but in an independent leukemic clone. This is due to a.
For example carriers of Robertsonian translocations involving chromosome 21 have a higher risk of having a child with Down syndrome.

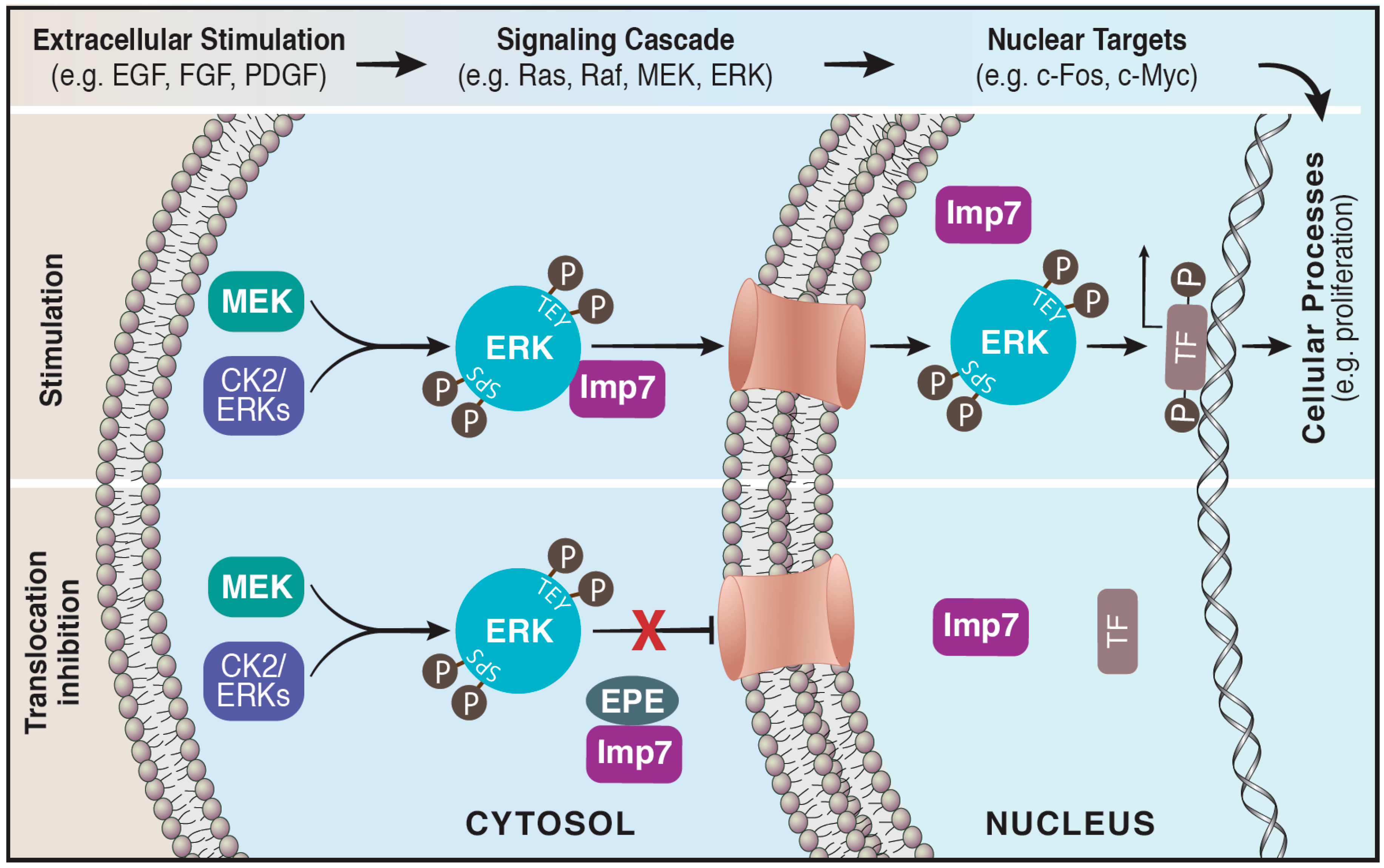
Ijms Free Full Text Nuclear Erk Mechanism Of Translocation Substrates And Role In Cancer Html

The Consequences Of Recurring Chromosome Translocations Learn Science At Scitable

The Bcr Abl1 Gene Chromosomal Translocation Dna Genetics Molecular Biology
Comments
Post a Comment